There are many 3D printing materials on the market, and it is important to know that you’re not limited to the base materials. An important additive option is carbon fiber, which can be used to strengthen base materials. Although it can be used in SLS 3D printing as well, this article will focus on carbon fiber composite filament for FDM 3D printing. In this article, we’ll discuss what carbon fiber is, how it relates to 3D printing, and its pros and cons.
 What is Carbon Fiber?
What is Carbon Fiber?
Carbon fiber is essentially a thin strip of carbon atoms bound together in a rigid crystal formation. Alone, these fibers are not very strong as they are brittle and can be easily snapped. However, if woven together into sheets or otherwise used en masse, the resulting part can have quite a high tensile strength. Heavy loads will be evenly distributed across all fibers when used together like this. In addition to its strength, carbon fiber has a high strength-to-weight ratio, meaning that parts made with carbon fiber have a strength-to-weight ratio comparable to aluminum.
How is Carbon Fiber Used in 3D Printing?
To produce stronger parts with 3D printing, lower-grade materials can be combined with carbon fiber to form a composite filament that is used by FDM 3D printers. It is important to note that this is not Continuous Fiber Fabrication, or CFF, which uses whole fibers embedded in material. Rather, this composite filament utilizes a thermoplastic mixed with chopped carbon fiber pieces that are less than 1mm long, typically closer to 0.5mm. This small size is required because the carbon fiber does not melt during FDM extrusion as the thermoplastic does and, thus, the pieces must be much smaller than the diameter of the print head nozzle to avoid clogs. This composite filament is used the same as any other FDM filament, and the printing process is not majorly changed.
Carbon fiber composite filament may also be referred to as filled or reinforced plastic. Popular choices of carbon fiber filled materials are ABS, PLA, PEKK, PEEK, PETG, PEI, PC, Nylon, and more.
Advantages of Carbon Fiber Composite Filament
There are several advantages to using carbon fiber composite filament over un-reinforced filament.
 Increased Base Material Properties
Increased Base Material Properties
Carbon fiber is most commonly used as a strengthening additive, but it also improves the mechanical properties of the base thermoplastic in other ways. The enhanced characteristics include greater rigidity, dimensional stability, and chemical and temperature resistance. As such, lower-grade materials can be made more durable for a wider variety of applications simply by adding carbon fiber.
Lightweight Metal Replacement
The excellent strength-to-weight ratio of carbon fiber allows for the creation of sturdy, lightweight parts. Due to this, parts made from carbon fiber composite filament can act as a lighter alternative to metal, such as aluminum and more. It is also a much cheaper option than metal.
Prevents Shrinking
Carbon fiber composite filament also has low thermal expansion, meaning that 3D printed parts are less likely to suffer major shrinkage as they cool. This can help increase the quality of your part.
Disadvantages of Carbon Fiber Composite Filament
Although carbon fiber composite filament has many qualities that make it advantageous for many applications, there are some drawbacks that often present themselves during the printing process. However, there are often easy solutions to these problems.
Nozzle Destruction
Because the carbon fiber in a composite filament does not melt during extrusion, they are abrasive and can potentially ruin the 3D printer’s print head nozzle. This happens with standard brass and aluminum nozzles because the carbon fiber is harder than the nozzle material. To prevent this problem, carbon fiber composite filament must be printed with a hardened steel nozzle. However, while the hardened steel will not show wear, other adjustments must be made to the 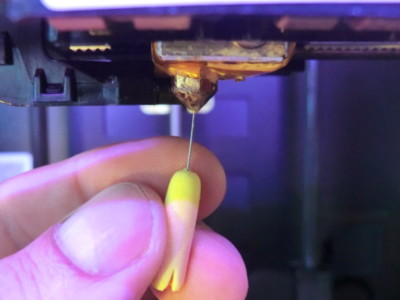 3D printer’s settings to accommodate this change. Hardened steel is less thermally conductive than brass, so the extruder temperature must be increased to ensure the filament melts correctly and doesn’t clog.
3D printer’s settings to accommodate this change. Hardened steel is less thermally conductive than brass, so the extruder temperature must be increased to ensure the filament melts correctly and doesn’t clog.
Clogging
Clogs are more likely to happen with carbon fiber composite filament than most other materials. Since the filament is brittle, it may snap on its path from the spool to the nozzle and result in a disrupted print. This is easily prevented by ensuring that the path is free of sharp turns and any areas where the filament may drag against another surface. Clogs may also result from the hard fiber being more difficult to push smoothly through the nozzle, meaning that buildup is more likely to occur. There are several ways to combat this, including reducing or disabling retraction, slowing the print speed, and using a nozzle with a larger diameter. Keep in mind, though, that adjusting retraction, speed, and nozzle diameter these ways may make it more difficult to achieve the desired print quality. The filament may have increased oozing, and a larger layer height due to nozzle size may degrade the finished quality of fine features.
Surface Finish
When purchasing carbon fiber composite filament, it is important to note that different companies mix different ratios of thermoplastic material and carbon fiber together to make their filaments. This can affect the surface finish quality of your print because, while lower amounts of carbon fiber may increase this quality, high amounts past a certain threshold will degrade it. As the percentage of carbon fiber increases, there is less and less plastic being used to create your part. This can result in a rough surface finish.
3D Printing at 3 Space
Here at 3 Space, we offer a variety of 3D printing services, including FDM, PolyJet, and MultiJet. If you have any questions regarding materials or services, our engineers will be happy to assist you. For more information, contact us today.
